Visual Perceptual Skills and Why They Matter for Learning
Affiliate and Referral links are used below to promote products I love and recommend. I receive a commission on any purchases made through these links. Please see my disclosure policy for more details. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
When we think about vision, we often think about eyesight, or how clearly a child can see. But there’s another important piece of the puzzle that often gets overlooked: visual perception.
What is Visual Perception?
Visual perception is the process by which the brain interprets and makes sense of what the eyes see. A child can have perfect eyesight and still struggle with visual perception skills. When addressing any challenges related to vision, a child should receive a comprehensive vision exam to rule out any actual vision problems. So keep that in mind before addressing any visual-perception or visual-motor challenges.
What is Visual-Motor vs. Visual-Perception?
Speaking of visual-motor, what is the difference between visual-motor and visual perception?
Visual perception is the brain’s ability to recognize, organize, and understand visual information. It helps children notice details, see similarities and differences, understand spatial relationships, and recognize patterns. Visual perception is about understanding what you see.
Visual-motor integration is about using what you see to guide movement.
You can read more in my What is Visual Perception post here.
How Visual Perception Impacts School and Daily Life
Visual perceptual skills play a big role in many activities, including:
- Recognizing letters, numbers, and shapes
- Copying from the board or a worksheet
- Finding items on a busy page
- Completing puzzles and games
- Understanding math concepts like patterns and spacing
- Organizing work on paper
7 Key Skills of Visual Perception
Visual perception is made up of seven different skills that work together to support reading, writing, math, play, and everyday independence.
Let’s take a closer look at the first four and how you can support them through simple, playful activities.
1 || Visual Discrimination
Visual discrimination is the ability to notice similarities and differences between shapes, letters, numbers, or objects while ignoring background “visual noise.”
This skill helps children tell the difference between letters like b and d, spot details in pictures, and find the correct answer on a worksheet.
Try this:
- Matching and memory games
- “Spot the difference” pictures
- Sorting objects by shape, size, or color
- Finding specific letters or numbers in a book or magazine
2 || Visual Memory
Visual memory is the ability to remember what has been seen after it’s no longer in view. This skill supports letter recognition, spelling, copying from the board, and reading fluency.
Learning to write depends on remembering visual patterns and translating them from memory onto the page.
Try this:
- Memory card games
- Show a picture briefly, hide it, and ask what was seen
- Copying block or building brick designs after viewing them
- Drawing a picture from memory
3 || Visual Spatial Relationships
This skill helps children understand where objects are in space and recognize objects even when they’re turned, flipped, or positioned differently.
Visual spatial skills also support body awareness and movement, relying on visual, vestibular, auditory, and proprioceptive systems working together.
Try this:
- Building block designs from a model
- Puzzles
- Copying patterns or shapes
- Games using position words like over, under, beside, left, and right
4 || Visual Form Constancy
Visual form constancy allows children to recognize shapes, letters, or numbers even when they change in size, color, or font.
This is important for reading different fonts, recognizing letters in new contexts, and matching objects accurately.
Try this:
- Matching letters or shapes in different sizes or fonts
- Finding letters or shapes in books, signs, or the environment
- Sorting objects that are the same shape but look different
- “I Spy” games using shapes or letters
5 || Visual Sequential Memory
Visual sequential memory is the ability to remember a series of visual items in the correct order. This skill supports spelling, reading, math steps, and remembering patterns.
Try this:
- Copying patterns or bead sequences
- Recreating block designs in order
- Remembering and drawing a sequence of shapes
- Playing “repeat the pattern” games
6 || Visual Figure/Ground
Figure-ground perception is the ability to find something specific in a busy background. This skill is essential for locating words on a page, finding items in a desk, or spotting information on worksheets.
Try this:
- Hidden picture books or worksheets
- “I Spy” games
- Finding specific objects in a sensory bin
- Highlighting important information on worksheets
7 || Visual Closure
Visual closure is the ability to recognize an object or form when only part of it is visible. This helps children read fluently and understand incomplete visual information.
Try this:
- Guess-the-picture games with partially covered images
- Puzzles with missing pieces
- Identifying incomplete shapes or letters
- Finishing partially drawn pictures
These seven visual perceptual skills don’t work alone. Together, they support visual-motor integration, fine motor development, handwriting, reading, math, and classroom success. Visual perceptual skills can be strengthened through play and everyday activities.
I hope this gives you a better picture of visual perception and how visual-integration is an important piece of child development.
Are you ready to take a deeper look at this important skill?
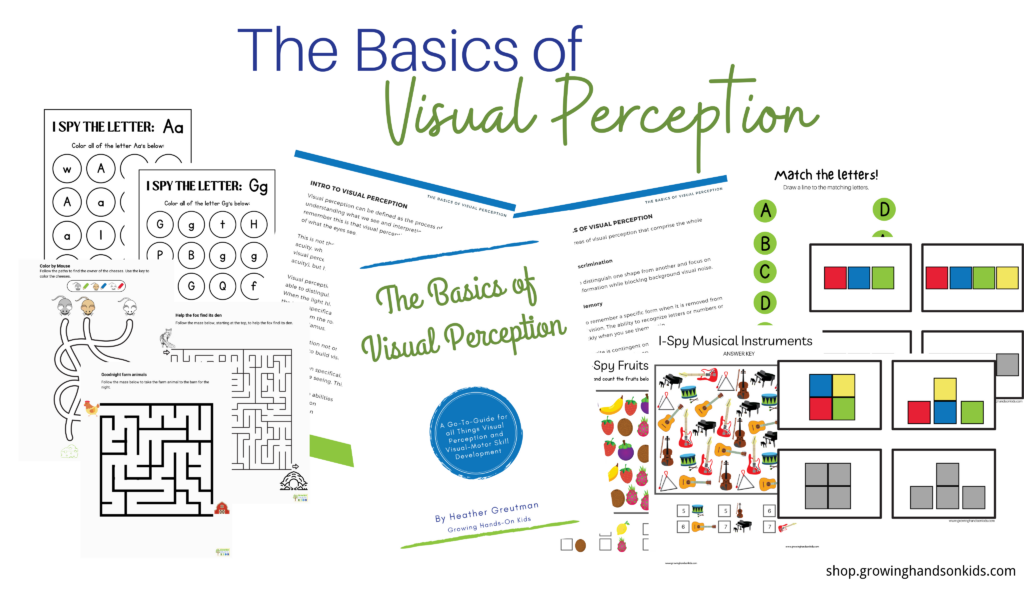
That’s why I created The Basics of Visual Perception: a friendly, go-to resource that takes the mystery out of visual perception and gives you practical tools to help kids thrive.
What's inside:
- A clear explanation of visual perception and the 7 categories of visual-perceptual skills
- Visual-motor development milestones for ages 0–6 (perfect for quick reference!)
- How visual-motor integration works and why it matters for learning
- Engaging activities to strengthen skills across all ages and settings
- A handout of visual-motor milestones you can share with parents and teachers
- Printable worksheets to build visual-perceptual skills through play and practice
Get your copy today and make supporting visual skills easier, more engaging, and effective!
You May Also Like:
- Visual Perceptual Skills Needed for Independent Feeding
- Typical Visual-Motor Development in Children
- The Foundational Skills Needed for Handwriting Mechanics
- Fun Summer-Themed Visual Motor Activities for Kids

Heather Greutman, COTA
Heather Greutman is a Certified Occupational Therapy Assistant with experience in school-based OT services for preschool through high school. She uses her background to share child development tips, tools, and strategies for parents, educators, and therapists. She is the author of many ebooks including The Basics of Fine Motor Skills, and Basics of Pre-Writing Skills, and co-author of Sensory Processing Explained: A Handbook for Parents and Educators.